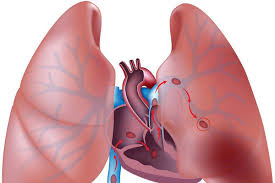
A pulmonary embolism occurs when a blood clot gets stuck in a pulmonary artery inside your lungs. The blood clot forms in your leg, or another vein deep inside your body and travels through your circulatory system until it can’t go any further and is trapped inside your lung.
If a pulmonary embolism is left untreated, it can be fatal. If you know the risk factors of a pulmonary embolism, you can seek medical treatment in time.
Who is at Risk for a Pulmonary Embolism
One of the most significant risk factors for a pulmonary embolism is a family history of blood clots or blood clot disorders. Other risk factors for developing pulmonary embolism include:
- Heart disease: cardiovascular disease, especially heart failure
- Cancer: undergone chemotherapy
- Recent Surgery
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Immobile for a prolonged period of time: often occurs if you have been hospitalized, put on bed rest, or during a long flight or car ride
- Birth control pills
- Smoking
- Pregnancy
If you are at risk for a pulmonary embolism, then it is imperative that you speak with your doctor about how to prevent a blood clot from forming.
What are the Signs of a Pulmonary Embolism
The signs and symptoms of a pulmonary embolism will vary. The symptoms will depend on the severity of the clot and where it is located. If you suffer from these symptoms, then you should seek medical help immediately:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Cough (with blood or bloody streaks in the stuff you cough up)
Other symptoms you might experience include:
- Leg pain or swelling (or both)
- Lightheaded
- Dizzy
- Clammy or discolored skin
- Blue lips or nails
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat
- Fever
- Sweating more than usual
If you are suffering from any of the symptoms associated with a pulmonary embolism, you should seek medical help right away.
How Can You Prevent a Pulmonary Embolism
You can reduce your risk of pulmonary embolism the same way you can stave off heart disease. If you smoke, find a smoking cessation program that works and keep trying. Understand that quitting takes practice and be patient with yourself. Avoid situations that force you to remain seated for hours on end. Maintain a healthy weight by building a logical diet and exercise program.
Exercise doesn’t have to feel boring or punishing. You can get your blood moving with a daily dance habit that will lift your spirits and put your heart to work. If you find yourself sitting for most of the day, find a way to break up that pattern with a short walk around the block or by taking a couple of flights of stairs.
What are the Treatment Options for a Pulmonary Embolism
The first thing your doctor will do to treat your pulmonary embolism is to prescribe medicine for a pulmonary embolism. The prescribed medicine will include:
- Anticoagulation: Blood thinners are used to prevent new clots from forming and also keep any clots from enlarging. Heparin is one of the popular choices for treating an embolism. Heparin is administered through an IV or injection for a faster therapeutic effect. Other types of oral anticoagulants include Warfarin, Xarelto, Pradaxa, and Eliquis.
- Clot dissolvers (thrombolytic): The drug speeds up the breakdown of a clot. It is only used for emergencies because of the dangerous side effects (can cause sudden bleeding). Prescribed if you have large clots that cause serve symptoms or serious complications.
If drugs don’t help dissolve your clot, you might need surgery. Some possible surgical options include:
- Vena cava filters : Are also viable treatment options for some people. The filter is inserted into the vena cava, a large vein in the patient’s body, and left in place to prevent blood clots from forming.
- Clot removal: A catheter is inserted and suctions out large clots from your artery. Not always effective, so this is not a preferred treatment method for most cases.
- Open surgery: Only used in emergencies. Doctors only use this option when the person is in shock or medications aren’t working.
Whether you are prescribed medication or need surgery, you should continue to see your primary physician on a regular basis for check-ups to ensure you remain healthy.
Final Thoughts
Even though a pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening, it is crucial that you know the risk factors, symptoms of potential blood clots, and when to seek medical attention. This way, you can ensure you resolve the problem before it becomes more problematic.