From crypto jacking to piggybacking, the world is staring at a whole new breed of cyber-security threats. Website owners have more reasons to be concerned than ever before.
Content management systems like WordPress, Joomla, Drupal, etc. which use a wide variety of third-party plugins and extensions are at more risk of being intercepted by hackers. The worst part is that most webmasters do not give cybersecurity the importance it needs, or they might unaware how to improve their website security.
This blog solely aimed for such users, who want to raise a wall of defense today, against cybersecurity attacks of tomorrow.
Without much ado, let’s get started.
1. Update Website Plugins & Extensions:
Do you remember the WannaCry ransomware that took millions of computers hostage? Well, it happened because too many users failed to download their security updates on time.
Updating your themes, plugins or your security databases is such a little task. There should be no reason to put it off unless you want your website to one among the millions that are taken over by hackers. Updates help fix the leaks in your site through which hackers can sneak in. It is no wonder that the tech boffins at WordPress and other CMS platforms keep releasing updates now and then.
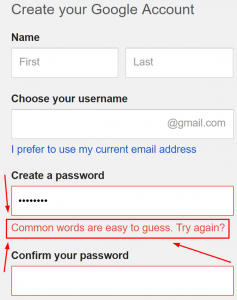
2. Avoid Easy-to-Guess Passwords:
Birthdates, license plate numbers, 123456, password, etc. do not deserve to be called passwords. They are so easy to guess that it is like leaving the keys to your home bang on the doorstep.
Avoid those easy-to-guess passwords right away and replace them with something that has the following characteristics:
- A password should be at least 8+ characters in length
- They should contain a combination of alphabets, numbers and special characters
- A password should change periodically
- A group of people should not access a password
3. Change Your Default CMS Settings:
Your default CMS settings are meant to make your login process more comfortable. They are not intended to keep your website secure. For instance, the admin panel would probably have ‘admin’ as the username. A hacker who is well-versed in brute force attacks would be able to penetrate your admin panel and take down the entire website effortlessly.
4. Use HTTPS-Encrypted Connection:
Secure your data and online transactions with SSL certificate because SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) used to establish HTTPS connection. So it can’t access by hackers. SSL certificate will be issued to the domain name (FQDN) after validation process followed by Certificate Authority. All data transmission will be protected between a web browser and a web server with 256-bit SSL encryption. So, you improve your website security from possible Main-In-The-Middle attacks, snooping, or data interception. We recommend CA trusted RapidSSL certificate for website conducting low volume online transactions. You can obtain Extended validation SSL to gain customers’ trust with your site.
5. Prevent Access to Sensitive Files
Your website would have several web server configuration files that determine how your site would appear and function to several users. If your website is running on an Apache web server, it would have a .htaccess file and nginx.conf if it is running on a Nginx server. Microsoft IIS servers have web.config etc..
These files are available in the root web directory. If left unprotected, unauthorized users can gain access to them and take malicious actions like running server rules, changing the website content, preventing users from accessing the website or taking it down completely.
Few ways how you can ensure that your website’s configuration files protected include:
- Preventing directory browsing
- Preventing image hotlinking
- Safeguarding sensitive data with passwords & encryption
6. Restrict File Permissions:
File permissions are like user privileges. It decides who can perform what kind of action on your website. Each file has three types of access permissions: Read, Write and Execute. Each of these permissions is indicated by numbers 4,2 and 1.
There are also three types of user types namely, owner, group and public each with their privileges. As a webmaster, you must ensure that the right user group is getting the deserving file permission. It helps eliminate any possibilities of security breaches.
7. Scrutinize Your Extensions/Themes:
As much as you like and enjoy using extensions for a site, there is an equal amount of risk involved in using them. Outdated extensions and themes running in your website’s background can allow hackers to make backdoor entries and take control of your site.
Take special care to ensure that the extensions and themes updated on a regular basis. If you are not using them any longer, uninstall them right away. It would at least help in making your website load faster.
8. Take Regular Backups:
Backups ensure that you have a support system to lean on in case your data is lost or damaged in a security breach. Ideally, all webmasters must have a regular backup plan in place. You should backup of specific modules every week, month or quarterly. This backup can be safely stored in offline storage devices or on the cloud where they are far from the reach of hackers.
CONCLUSION
Website security is something that every webmaster must be knowing and dealing with on a regular basis. They must understand its importance, the benefits it can bring to a business and