MRI, which stands for magnetic resonance imaging, has revolutionized medical diagnostics since its introduction in the 1970s. MRI services like Prp Imagaing or MRI scanners use powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed cross-sectional images of internal organs and tissues. This non-invasive technology is one of the most versatile medical imaging tools available today due to its many uses and ability to scan virtually all areas of the human body.
Brain and Spinal Imaging
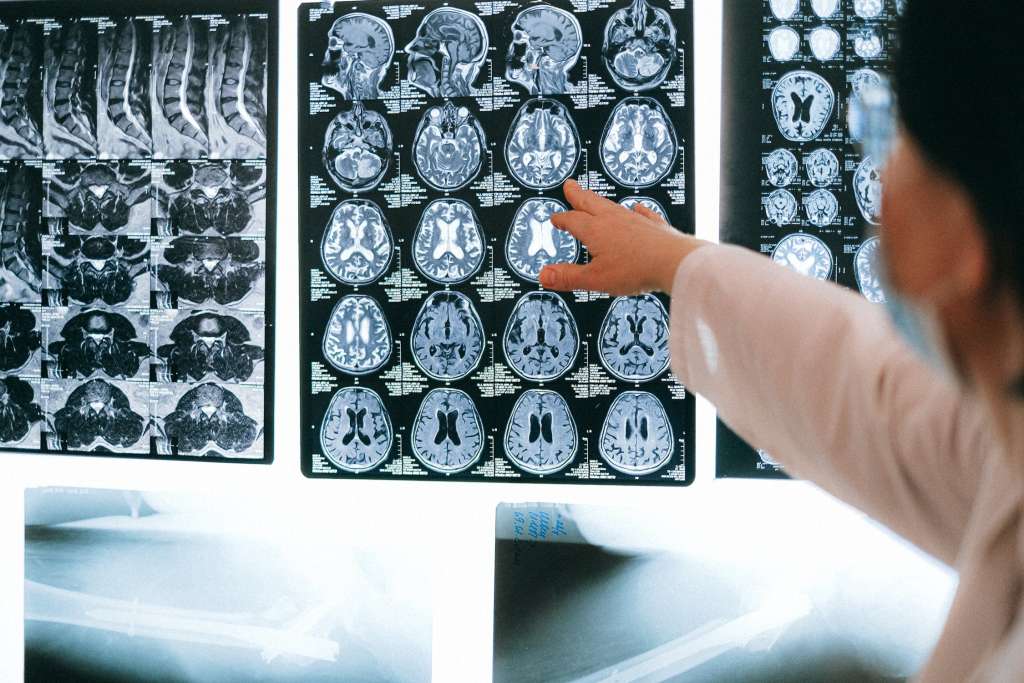
One of the most common uses of MRI scans is to image the brain and spinal cord. MRI produces very clear pictures of the brain’s structure and can detect minute abnormalities that may indicate things like brain tumors, bleeding, infections, multiple sclerosis, stroke, aneurysms, and nerve disorders. MRI is especially useful for imaging the posterior fossa and brainstem, areas difficult to see clearly on a CT scan.
MRI is also the preferred way to diagnose disorders of the spinal cord and surrounding areas like disk disease, spinal tumors, bone spurs, vascular malformations, infections, and injuries. MRI can image the spinal cord much better than regular x-rays or CT scans.
Joint and Musculoskeletal Imaging
MRI technology is often used to diagnose joint and musculoskeletal problems in areas like the shoulders, hips, knees, hands, and feet. It provides sharp images of soft tissues like cartilage, tendons, ligaments, muscles, and blood vessels—important parts of the musculoskeletal system that are poorly visualized on other imaging tests.
MRI is very useful for finding bone and joint abnormalities. Doctors often order MRI scans to diagnose things like sports-related injuries, carpal tunnel syndrome, rotator cuff tears, bone fractures, arthritis, bone tumors, infections, and congenital disorders. The information from an MRI helps doctors determine the best course of treatment.
Cancer Detection and Staging
One of the earliest uses of MRI was for improved cancer detection and staging. An MRI scan can often find tumors that may be obscured on an X-ray or CT scan. MRI is especially helpful for imaging organs like the brain, breast, uterus, prostate gland, colon, rectum, liver, pancreas, kidney, and bladder. Using specialized contrast dyes, physicians can spot tumors in MRI scans based on differences in blood flow and cell metabolism between normal and malignant tissues.
Once cancer is detected, an MRI can help doctors determine how advanced the cancer is by seeing if and where the tumor has spread to other parts of the body. Accurate staging of the cancer is key for effective treatment planning. Often, chemotherapy, radiation, or surgery plans are based on MRI findings.
Pregnancy and Fetal Medicine
While CT scans and X-rays are discouraged during pregnancy due to radiation risks, MRI is considered generally safe and is routinely used for the evaluation of many pregnancy-related conditions. MRI gives great insight when there are issues related to the uterus, placenta, amniotic fluid, or cervical competence. MRI is also used to track fetal development, detect birth defects, diagnose complications, assess anomalies of the pelvis and cervix, and manage other concerns that arise during gestation.
Conclusion
The uses of MRI technology have expanded greatly since its beginnings nearly 50 years ago. Continued enhancements promise additional medical applications in the future. MRI is now an indispensable tool for modern medicine, thanks to its versatility, sensitivity, and lack of radiation. It will likely remain a vital diagnostic imaging technique for many years to come.