3D printing is rapidly penetrating into our lives with each passing day. Initially, it came with mobile phones and even earlier with computers. Now, it is making advancements in the field of IT and medical.
With the help of this technology, it is possible to reproduce highly accurate three-dimensional models of human organs and implants. It helps a lot in medication. Here are 5 major achievements of 3D printing in medical field-
1. 3D Technologies: Tomography
Computed tomography of 3D technology is used for the diagnosis of diseases. Three-dimensional scanning gradually displaces film plane images. These devices have a high potential and are actively used in dental research, maxillofacial surgery. They allow you to diagnose diseases easily and facilitate the effective delivery of medical services to needy patients and clients.
3D tomography is a modern standard for diagnosis, which allowed the quality of diagnostics and treatment to reach a whole new level. The advantage of 3D shots is the ability to identify defects that are often neglected in conventional images. This enables us to determine the complex morphology of problem areas and establish a more precise treatment. 3D tomography is a high-quality image with minimum irradiation. It also increases the speed of study and diagnosis up to a great extent without any hassle.
2.3D-Bioprinter For The Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus
In early December 2017, the Australian University of Wollongong presented a new customizable 3D bioprinter that can improve the treatment of patients with type 1 diabetes. The inventors called the system a 3D bioprinter for pancreatic cell transplantation (PICT). The new technology was presented to the Health Minister of South Australia and then transferred for use to the Royal Adelaide Hospital.
The developers maintain that the system applies special biochanin, containing insulin-producing islet cells, on transplantable 3D-printed frame structures. It is expected that this method should improve the existing islet cell transplantation process from human donors used to treat serious cases of diabetes.
The new technology reduces the risk of rejection of the transplanted tissue by incorporating the patient’s cells into the donor tissue. In addition, the bioprinter prints several types of cells. So, its framework structure can also include endothelial cytes necessary for the growth of new blood vessels in the transplanted islet tissue.
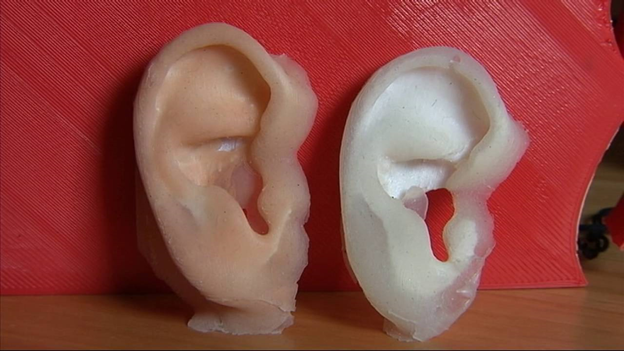
3. 3D Printing of The Middle Ear For Hearing Return
At the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA) in December 2017, it was shown how using 3D printing it is possible to reproduce exact copies of the middle ear for the return of hearing to people. Development began to be applied in practice. By converting 3D images, surgeons succeeded in placing exactly four implants of different sizes into the human ears.
According to the scientist, this method can improve the surgical procedure, which often fails due to the wrong size of prosthetic implants. In the study, four surgeons performed implants in four different middle ears. They were able to accurately combine the prosthesis model with a temporal bone containing the middle and inner parts of the ear. The chances for such an outcome with conventional prosthetics are 1: 1296.
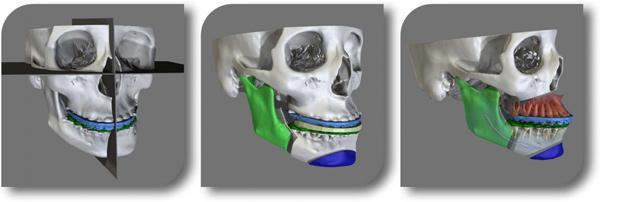
4. 3D Modeling: Medicine
Three-dimensional models created on the basis of computed tomography in combination with three-dimensional printing are an indispensable achievement in the field of medicine. 3D modeling in medicine allows you to create three-dimensional models. Three-dimensional images of patients, made with computed tomography, are transformed into an image with a good resolution, and then into solid 3D models.
This allows you to study the characteristics of the disease and prepare well for the operation. So, for a surgeon, it is important to know the shape, outlines, features of the tumor in the three-dimensional dimension, in order to know how to act better during the operation.
With the use of 3D technologies, complex operations are performed as per the following scheme:
- Scanning,
- Manufacturing of plastic model,
- Study and choice of treatment and
- Actual treatment
3D printers are used in conjunction with modern design systems. So, with their help, print the clone of the tumor before the operation so that you may what you are going to face next time and prepare yourself for the operation.
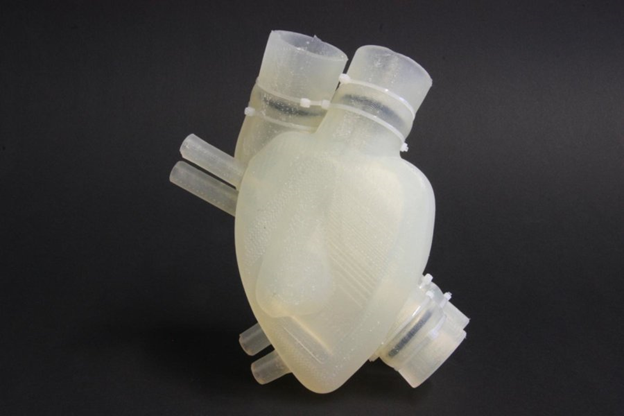
5. Print of Artificial Heart
In July 2017, the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zurich (ETH Zurich) presented an artificial heart created using 3D printing. At the time of the announcement, the product made of silicone was far from the stage of commercial readiness.
An artificial heart weighing 390 grams and a volume of 679 cubic centimeters are printed on a 3D printer by the method of investment casting. The left and right ventricles are not separated by a septum but filled with compressed air through a special chamber. Puffing and bloating, this camera mimics the contraction of the muscles of the human heart and pumps blood.
For the time being, the artificial heart supports only 3000 strokes. It can work for 30 to 45 minutes. To test the work of the heart, scientists used an advanced test environment that mimics the human cardiovascular system and a fluid that has a viscosity comparable to that of blood.
By 2017, about 26 million people suffered from heart failure. Most of them are hopelessly waiting for donors to provide them with a new heart. Such patients are provided with special blood pumps that facilitate the work of the heart. But, they can cause serious complications and do not provide patients with a pulse.
Final Words:
3D printing has several medical miracles. These 5 have helped the medical industry to diagnose complex diseases easily and cure them quickly without any problem.
Author Bio:
David Blakey is a blogger by profession with 5 years of experience. He is associated with Hot Toner, selling Canon mg2560 ink cartridges online in Australia. He is an admirer of sharing his innovative ideas with others on the technology trends.